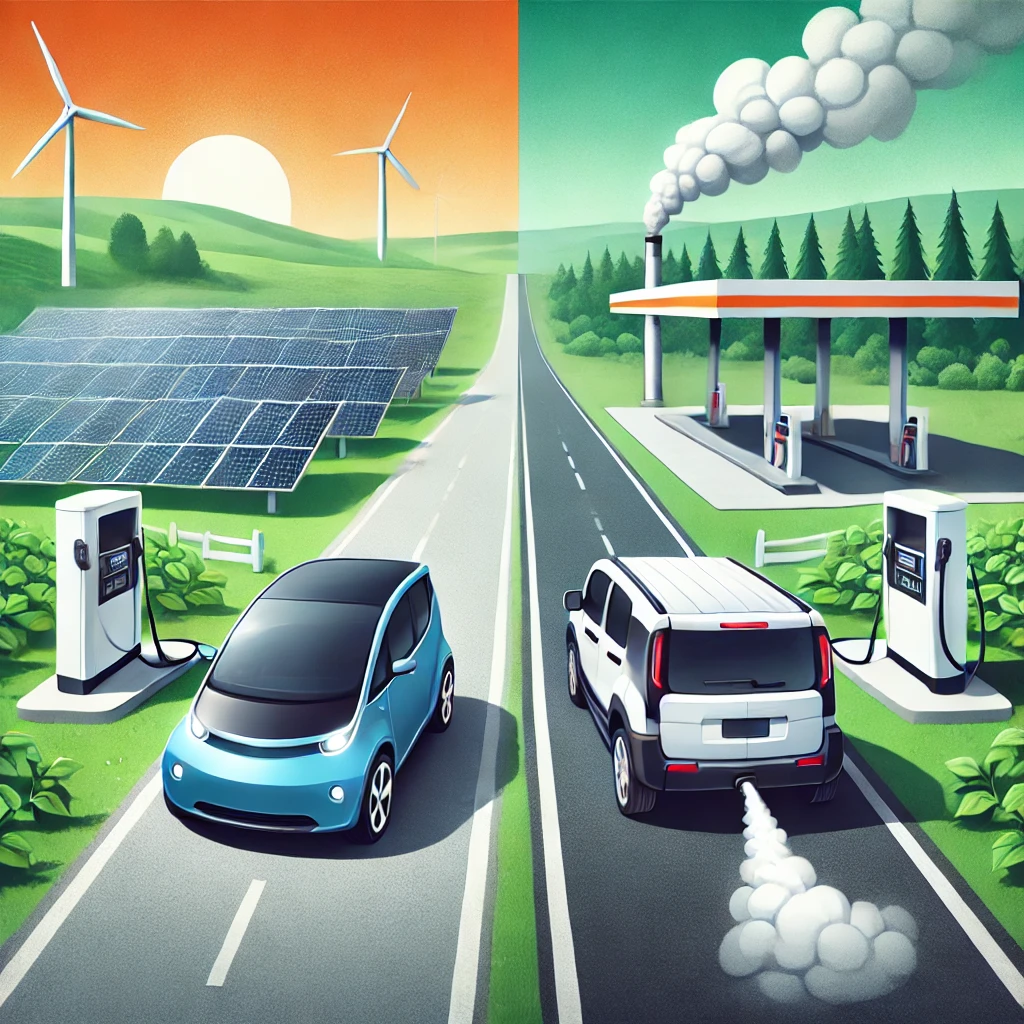
As the world increasingly turns its attention to combating climate change, the debate between electric vehicles (EVs) and traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles—often referred to as oil vehicles—has gained momentum. Both types of vehicles serve the same fundamental purpose, but from an ecological perspective, they have vastly different impacts on the environment. Let’s delve into the comparison of Electric Vehicles vs. Petrol Vehicles in terms of their environmental effects.
1. Carbon Emissions
One of the most significant ecological advantages of electric vehicles is their potential to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. EVs produce zero tailpipe emissions, which means they do not directly emit pollutants like carbon dioxide (CO2), nitrogen oxides (NOx), or particulate matter. In contrast, oil vehicles release CO2 and other harmful emissions that contribute to global warming and air pollution.
However, it is essential to note that the overall environmental impact of EVs also depends on the energy source used to charge them. If an EV is charged using electricity from coal-powered plants, its carbon footprint will be higher than if it is charged from renewable energy sources like solar or wind.
2. Manufacturing Process
While EVs excel in reducing emissions during operation, the ecological cost of manufacturing them, particularly their batteries, is higher than that of oil vehicles. Lithium-ion batteries, which are essential for EVs, require the extraction of raw materials like lithium, cobalt, and nickel. Mining for these materials can have negative ecological impacts, including habitat destruction, water contamination, and increased carbon emissions.
Oil vehicles, on the other hand, rely on the extraction and refinement of crude oil, a process that has its own set of environmental challenges, such as oil spills, air pollution from refineries, and ecosystem disruption.
3. Energy Efficiency
Electric vehicles are inherently more energy-efficient than oil vehicles. EVs convert about 60-77% of the electrical energy from the grid into power at the wheels, whereas oil vehicles only convert about 12-30% of the energy from gasoline into power. This higher energy efficiency means that EVs require less energy to travel the same distance, resulting in lower overall energy consumption and fewer emissions over the vehicle’s lifetime.
4. Air Pollution
Another ecological win for EVs is their contribution to reducing air pollution, especially in urban areas. Oil vehicles emit pollutants such as NOx and particulate matter, which contribute to smog and respiratory problems. In contrast, EVs do not emit any of these pollutants, improving air quality and reducing health risks.
5. End-of-Life and Recycling
When it comes to the end-of-life stage, EVs pose a unique challenge. While the batteries can be recycled, the process is not yet as widespread or efficient as traditional vehicle recycling systems. Battery recycling requires specialized facilities, and improper disposal can lead to environmental hazards such as soil and water contamination. However, innovations in battery recycling technologies are evolving rapidly, which could make EVs even more ecologically advantageous in the future.
Oil vehicles, while more straightforward to recycle, are still reliant on fossil fuels during their operational lifetime, which continues to contribute to environmental degradation even after the vehicle is scrapped.
6. Fuel Source and Availability
The use of renewable energy in EV charging infrastructure is a game-changer for the environment. As more countries invest in renewable energy sources, such as wind, solar, and hydropower, EVs will increasingly be powered by clean energy, making them more sustainable. In contrast, oil vehicles depend on a non-renewable resource—crude oil—that contributes to deforestation, water pollution, and climate change.
Conclusion
From an ecological perspective, electric vehicles offer significant advantages over oil vehicles, especially in terms of reducing carbon emissions, air pollution, and energy consumption. However, the production and disposal of EV batteries present challenges that need to be addressed to maximize their environmental benefits. On the other hand, oil vehicles remain a major contributor to environmental degradation due to their reliance on fossil fuels and higher emissions.
As technology evolves and the world shifts toward renewable energy, electric vehicles are poised to play a crucial role in creating a more sustainable and environmentally friendly transportation system.