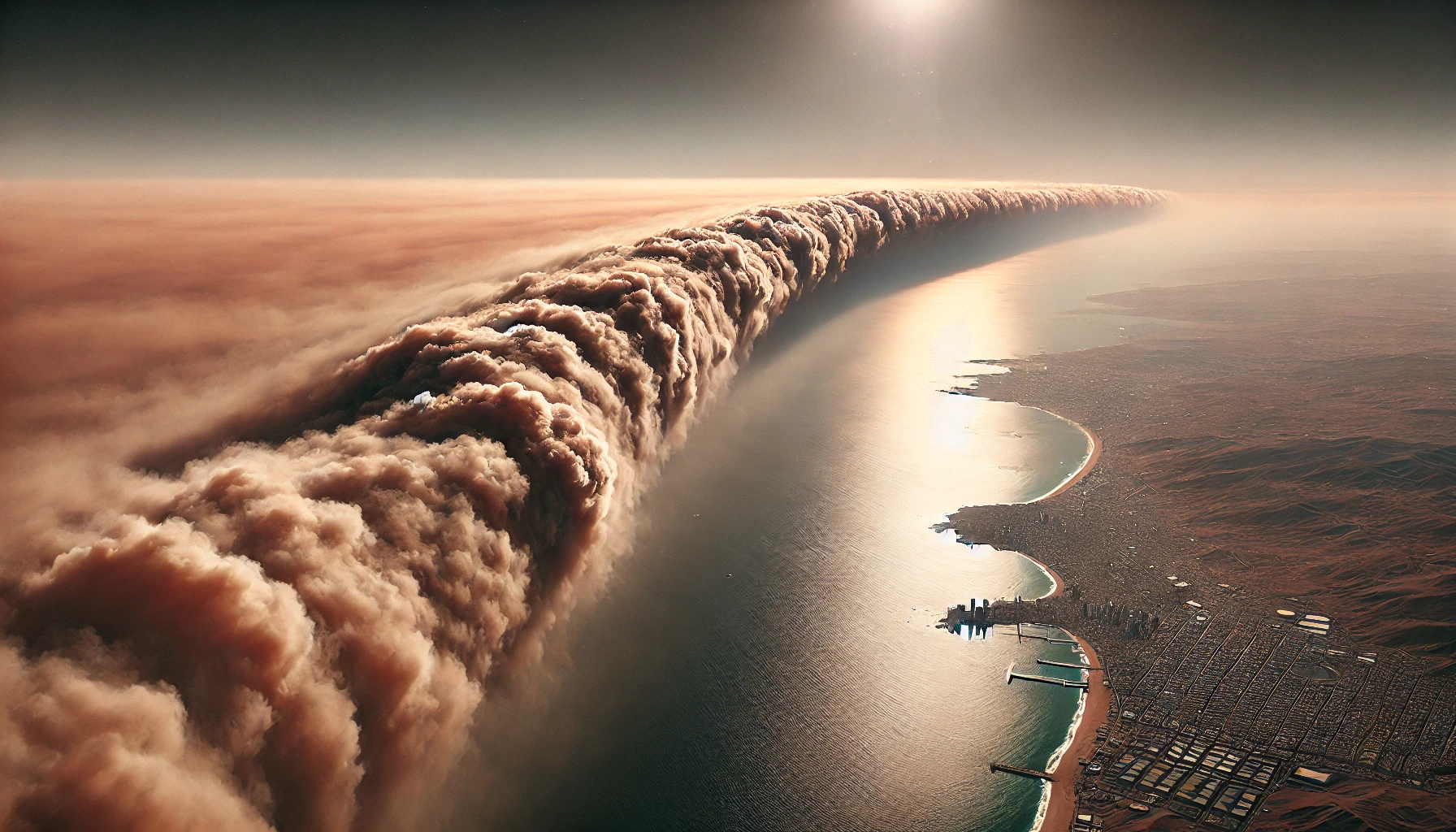
Every year, vast amounts of dust rise from the Sahara Desert, traveling thousands of miles across the Atlantic Ocean. This natural event, known as the Sahara Dust Cloud, plays a significant role in shaping air quality, weather patterns, and even ecological systems worldwide. Let’s explore how and why the Sahara Dust Cloud forms and its impact on global air quality.
What is the Sahara Dust Cloud?
The Sahara Dust Cloud refers to a massive plume of dust that originates from the Sahara Desert in North Africa. This dust cloud is carried by strong trade winds, known as the Saharan Air Layer (SAL), and can travel as far as the Caribbean, the Americas, and parts of Europe. The dust particles contain a mixture of minerals, such as iron, silicon, and phosphorus, that impact various regions as they settle.
How the Sahara Dust Cloud Forms
- Dry Conditions and High Winds
The Sahara Desert’s arid, dry conditions create loose sand and soil particles that are easily picked up by wind. When strong winds blow across the desert, they lift these particles into the air, creating dense dust plumes. - Trade Winds Carry the Dust
The trade winds, especially during the summer months, carry these dust clouds across the Atlantic. The Saharan Air Layer, a hot, dry air mass that sits above cooler ocean air, helps keep the dust particles suspended, allowing them to travel great distances.
Impact of the Sahara Dust Cloud on Air Quality
- Reduced Air Quality
When the Sahara Dust Cloud reaches other continents, it brings a surge of dust particles that can affect respiratory health. People with asthma, allergies, and other respiratory conditions may experience worsened symptoms during periods of high dust. - Weather and Visibility
The dust particles reduce visibility, creating a hazy sky that obscures sunlight. In some cases, the dust can reduce sunlight by up to 20%, impacting temperatures and even altering weather patterns temporarily. - Benefits for Ecosystems
Surprisingly, the Sahara Dust Cloud provides benefits as well. Dust from the Sahara is rich in minerals, which nourish soils in the Amazon rainforest and fertilize the ocean’s surface, helping support marine life and phytoplankton growth.
Regions Most Affected by Sahara Dust
The Sahara Dust Cloud is most prominent in regions close to its origin, such as North Africa, the Mediterranean, and parts of Southern Europe. However, it also travels to:
- The Caribbean and the Gulf of Mexico: Caribbean islands and the U.S. Gulf Coast often experience reduced air quality and hazy skies during peak dust season.
- South America’s Amazon Basin: Nutrient-rich dust helps replenish soil in the Amazon rainforest, supporting plant growth and biodiversity.
Climate and Long-term Effects
Some research suggests that the Sahara Dust Cloud may help offset global warming by reflecting sunlight away from the Earth’s surface. On the other hand, an increase in dust storms due to desertification could mean that more regions face the negative health and air quality impacts associated with the dust.
Conclusion
The Sahara Dust Cloud is a fascinating phenomenon with both positive and negative impacts. While it poses health challenges in affected regions, it also supports ecosystems far from its source, illustrating the interconnectedness of Earth’s natural systems. As climate patterns shift, monitoring the Sahara Dust Cloud and understanding its effects on air quality and ecosystems will be crucial.

2 thoughts on “The Sahara Dust Cloud: How African Dust Affects Air Quality Worldwide”