Fire rainbows, officially known as circumhorizontal arcs, are among the most breathtaking natural phenomena in the sky. This rare atmospheric effect produces vibrant, rainbow-like colors that appear to blaze across the clouds, creating the illusion of fire in the sky. Despite their name, fire rainbows are not true rainbows nor related to fire; they are optical illusions caused by sunlight passing through ice crystals. Here’s a closer look at how and why these stunning displays form.
What is a Fire Rainbow?
A fire rainbow, or circumhorizontal arc, is a type of halo that appears as a horizontal band of vivid colors near cirrus clouds. The effect occurs when sunlight enters hexagonal ice crystals at a particular angle, refracting and spreading the light into rainbow colors. The colors are typically brighter and more saturated than those seen in a regular rainbow, often resembling a vibrant flame spread across the sky.
How Fire Rainbows Form
- Ice Crystals in High-Altitude Clouds
Fire rainbows occur in cirrus clouds, which are high-altitude clouds made up of tiny ice crystals. These clouds are usually found at altitudes of 20,000 feet or higher, where temperatures are extremely cold. - Angle of the Sun
For a fire rainbow to appear, the sun must be high in the sky—usually at an elevation of at least 58 degrees above the horizon. This specific angle allows sunlight to enter the ice crystals at the correct orientation, bending the light to create the arc. - Refraction of Light Through Ice Crystals
When sunlight enters the flat, horizontal ice crystals, it is refracted, or bent, in such a way that it spreads into the colors of the spectrum. This bending process is similar to what happens in a prism, with each color separated based on its wavelength.
Where and When Can You See Fire Rainbows?
Fire rainbows are rare and are most often observed in mid-latitude regions during the summer months, when the sun reaches the necessary elevation. Countries in the northern and southern hemispheres at mid-latitudes, such as parts of the United States, Canada, and Europe, have higher chances of seeing them. The phenomenon is best observed on clear days with cirrus clouds and bright sunlight.
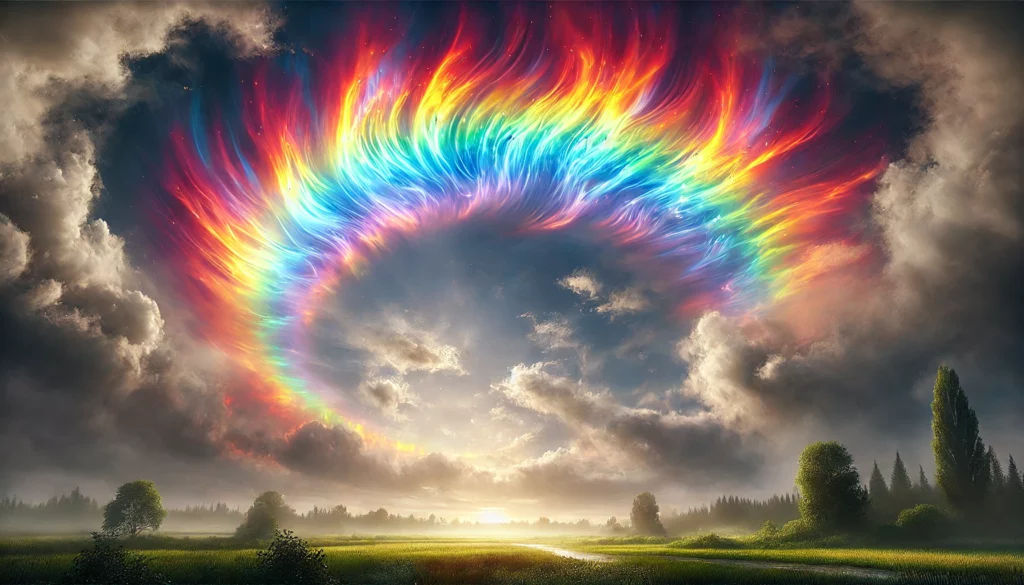

Why Fire Rainbows are So Rare
Fire rainbows are difficult to spot because they require very specific atmospheric conditions:
- High Sun Elevation: The sun must be at a high angle, which only happens at certain latitudes during specific times of the year.
- Presence of Cirrus Clouds: These clouds must contain the correct type and orientation of ice crystals.
- Clear Skies: The effect is best seen on clear days when cirrus clouds are thin enough to let sunlight pass through.
Fascination and Beauty of Fire Rainbows
Fire rainbows captivate viewers with their surreal, flame-like appearance. Because they are rare and fleeting, seeing a fire rainbow feels almost magical, adding to their appeal. Unlike traditional rainbows, fire rainbows are usually more vivid, with colors that appear brighter and more intense, giving the impression of a rainbow on fire.
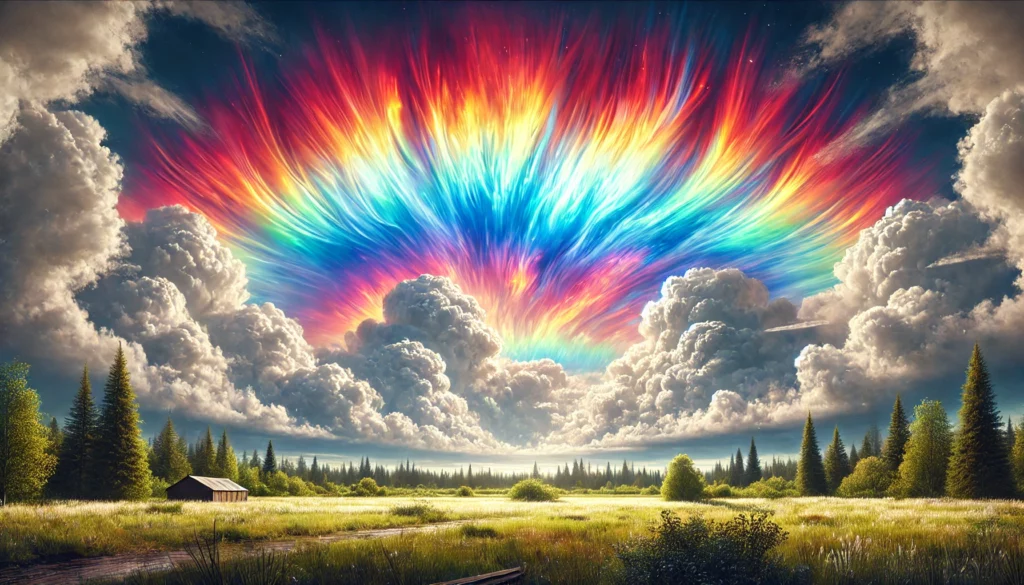

Conclusion
Fire rainbows, or circumhorizontal arcs, are a stunning example of nature’s artistry in the sky. Caused by the refraction of sunlight through ice crystals, these arcs of color provide a brief but beautiful spectacle for those lucky enough to witness them. Understanding the science behind fire rainbows helps us appreciate the unique conditions that create this rare phenomenon, reminding us of the incredible beauty in our atmosphere.

nice AI
still looks good