Ball lightning is one of the most fascinating and mysterious phenomena in atmospheric science. This rare and unpredictable occurrence has puzzled scientists and intrigued observers for centuries. Despite being documented throughout history, the exact cause of ball lightning remains elusive. In this article, we will explore the phenomenon of ball lightning, its characteristics, and the scientific theories that attempt to explain it.
What is Ball Lightning?
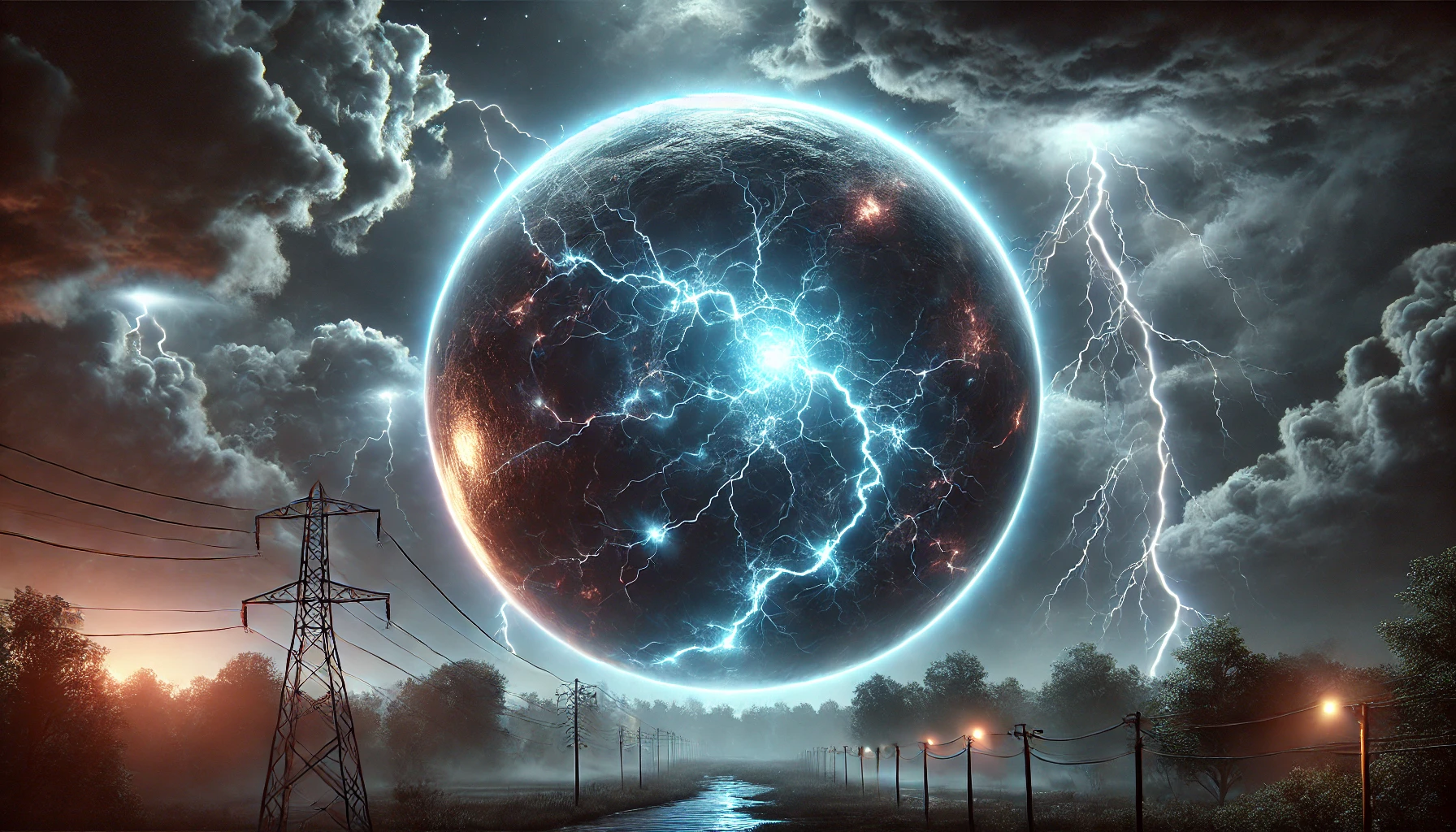
Ball lightning is a rare atmospheric phenomenon characterized by a glowing, spherical ball of light. These glowing spheres can range in size from a few centimeters to over a meter in diameter. The phenomenon is typically seen during thunderstorms and is often described as floating or drifting in mid-air, sometimes hovering near the ground or even traveling through windows. Unlike typical lightning, which is a sharp, instantaneous flash, ball lightning can last for several seconds to minutes.
The color of ball lightning can vary, with some reports describing it as blue, orange, or white. Some observers have even described the ball as having a faint crackling sound or emitting a sulfurous odor, making it both an eerie and captivating sight.
The Mystery Behind Ball Lightning
The science behind ball lightning remains one of the most intriguing mysteries in meteorology and physics. Despite numerous accounts from reliable witnesses, including pilots, scientists, and soldiers, no conclusive explanation has been universally accepted. Ball lightning’s transient and unpredictable nature makes it difficult to study, and the phenomenon has rarely been captured on film.
Over the years, several theories have been proposed to explain the occurrence of ball lightning:
- Plasma Theory: Some scientists believe that ball lightning is a type of plasma, a charged state of matter that exists at high temperatures. Plasma could explain the glowing, spherical shape of the phenomenon. In this theory, ball lightning is thought to form when ionized air or gases create a stable plasma ball that floats through the atmosphere.
- Electromagnetic Theories: Other researchers suggest that ball lightning could be the result of electromagnetic forces, created by the interaction of thunderstorm activity with the surrounding environment. This could include the influence of magnetic fields, ionization, and localized electrical currents.
- Microwave Theory: A more recent theory suggests that ball lightning might be related to microwave radiation. According to this idea, the energy generated by lightning could create a microwave discharge in the atmosphere, which could result in the formation of glowing spheres.
- Chemical Reaction Theory: Some theories propose that ball lightning is a result of chemical reactions, possibly involving silicon particles in the air reacting with oxygen during a thunderstorm. This would produce a glowing ball that behaves similarly to a fireball.
Despite these hypotheses, no theory has been universally accepted, and researchers continue to debate the true nature of ball lightning.
Where and When Does Ball Lightning Occur?
Ball lightning is a rare phenomenon, with occurrences typically reported during thunderstorms. It has been observed around the world, but it remains most commonly associated with areas that experience intense electrical activity, such as regions with frequent lightning storms.
Ball lightning is most often seen in rural or open areas, although it has been reported in urban settings as well. The phenomenon tends to appear unexpectedly, sometimes following a lightning strike, and can behave in strange ways. Some reports describe ball lightning passing through windows, doors, or even walls, while others mention it disappearing without a trace or exploding suddenly.
Ball Lightning and Its Dangers
While ball lightning is captivating, it can also be dangerous. In some instances, the phenomenon has been associated with fires, explosions, or damage to electrical equipment. The cause of such incidents remains unclear, but the electrical nature of ball lightning could potentially lead to hazards if it interacts with flammable materials or sensitive electrical systems.
Due to its unpredictability, scientists are particularly cautious about the risks associated with studying ball lightning. The phenomenon is rarely observed under controlled conditions, making it difficult to study its true behavior.
Conclusion: A Fascinating Mystery in Atmospheric Science
Ball lightning is one of the most intriguing and unexplained phenomena in atmospheric science. Despite centuries of sightings and various theories, scientists have yet to definitively explain its origin or behavior. As technology advances, researchers may one day unlock the secrets of this rare phenomenon, but for now, it remains one of nature’s greatest mysteries like the volcanic lightning.

1 thought on “The Oddity of Ball Lightning: A Strange and Rare Atmospheric Phenomenon”