Introduction
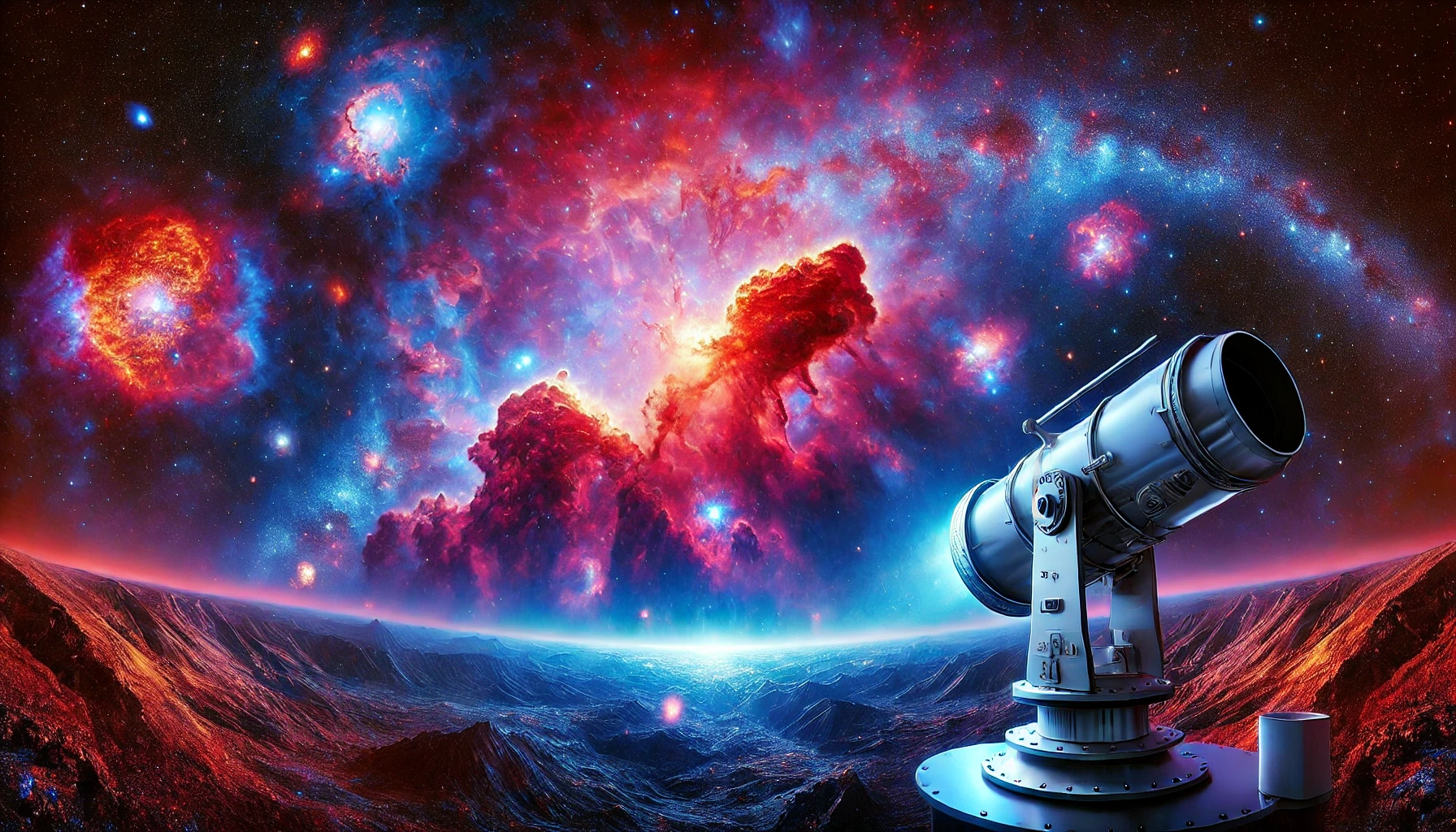
The universe is filled with colors beyond human vision. While our eyes perceive a narrow band of visible light, the cosmos reveals its wonders through infrared and ultraviolet wavelengths. By utilizing specialized telescopes, scientists can unlock the True Colors of the Universe, filled with phenomena invisible to the naked eye. This article explores how infrared and ultraviolet light help us understand celestial objects and their mysteries.
Understanding Light Beyond the Visible Spectrum
Visible light is just a small portion of the electromagnetic spectrum, which also includes radio waves, microwaves, infrared, ultraviolet, X-rays, and gamma rays. Infrared and ultraviolet light play a crucial role in astronomical discoveries:
- Infrared Light (IR): With longer wavelengths than visible light, infrared penetrates dust clouds, allowing astronomers to study hidden structures such as star-forming regions and distant galaxies.
- Ultraviolet Light (UV): With shorter wavelengths, ultraviolet light reveals high-energy cosmic phenomena such as hot young stars, nebulae, and supernova remnants.
How Infrared Light Unveils the Hidden Universe
Infrared telescopes detect thermal radiation emitted by celestial bodies, making them indispensable for studying:
- Star Formation: Infrared reveals newborn stars embedded in dense clouds of gas and dust.
- Distant Galaxies: Many ancient galaxies are so far away that their light is stretched into the infrared spectrum due to cosmic expansion.
- Exoplanets: Infrared helps in identifying planets orbiting distant stars by detecting their heat signatures.
Notable Infrared Observatories:
- James Webb Space Telescope (JWST): The most powerful infrared space telescope, capable of observing the earliest galaxies.
- Spitzer Space Telescope: Provided groundbreaking insights into planetary systems and star formation.
The Power of Ultraviolet Light in Astronomy
Ultraviolet light is crucial for studying energetic and extreme cosmic events. UV observations reveal:
- Hot Stars and Stellar Evolution: UV detects young, massive stars that burn at extremely high temperatures.
- Supernovae and Black Holes: Ultraviolet emissions help track explosive cosmic events and matter accreting around black holes.
- The Composition of Galaxies: UV surveys provide insights into the chemical composition of galaxies and star clusters.
Notable Ultraviolet Observatories:
- Hubble Space Telescope: Capable of capturing ultraviolet images of distant galaxies and nebulae.
- Galaxy Evolution Explorer (GALEX): Focused on mapping the ultraviolet sky to study star formation rates.
Why Infrared and Ultraviolet Observations Matter
By looking beyond visible light, astronomers can:
- Understand the lifecycle of stars and galaxies.
- Detect exoplanets and assess their atmospheres for potential habitability.
- Unravel the mysteries of dark matter and cosmic evolution.
Conclusion
The true colors of the universe extend far beyond what the human eye can see. By harnessing infrared and ultraviolet observations, scientists continue to push the boundaries of our cosmic understanding. As future telescopes expand our reach, we can expect even more breathtaking discoveries about the hidden wonders of the universe like the Northern Lights.